Bogosort

Este artigo apresenta apenas uma fonte. (Janeiro de 2024) |
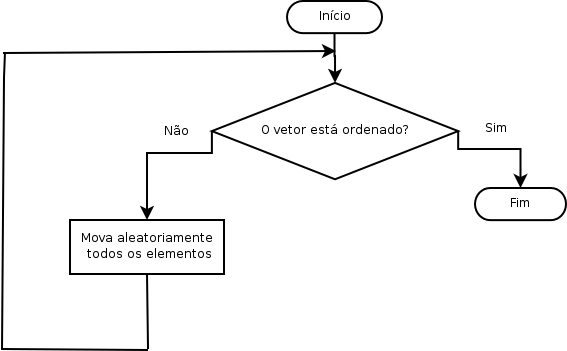
Bogosort (também conhecido como CaseSort ou Estou com Sort), é um algoritmo de ordenação extremamente ineficiente. É baseado na reordenação aleatória dos elementos. Não é utilizado na prática, mas pode ser usado no ensino de algoritmos mais eficientes. Seu nome veio do engraçado termo quantum bogodynamics e, ultimamente, a palavra bogus.
Esse algoritmo é probabilístico por natureza. Se todos os elementos a serem ordenados são distintos, a complexidade esperada é . O tempo exato de execução esperado depende do quantos diferentes valores de elementos ocorrem, e quantas vezes cada um deles ocorre, mas para casos não-triviais o tempo esperado de execução é exponencial ou super-exponencial a . Ele termina pela mesma razão do teorema do macaco infinito; existe alguma probabilidade de que aconteça a permutação correta, dado que em um infinito número de tentativas fatalmente a encontrará.
Deve-se notar que com os algoritmos geradores de números pseudo-aleatórios, que têm um número finito de estados e não são realmente aleatórios, o algoritmo pode nunca terminar para certos conjuntos de valores a serem ordenados.
Bogosort é um algoritmo de ordenação não estável.
Exemplo[editar | editar código-fonte]
Para se ordenar um baralho usando-se este Algoritmo, seria necessário jogar as cartas ao ar, juntá-las aleatoriamente, e então verificar se as mesmas estão ordenadas.
Algoritmo[editar | editar código-fonte]
função bogosort(array) enquanto não está_ordenado(array) array := permutação_aleatória(array)
Implementações[editar | editar código-fonte]
C[editar | editar código-fonte]
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <stdbool.h> bool is_sorted(int *a, int n) { while ( --n >= 1 ) { if ( a[n] < a[n-1] ) return false; } return true; } void shuffle(int *a, int n) { int i, t, r; for(i=0; i < n; i++) { t = a[i]; r = rand() % n; a[i] = a[r]; a[r] = t; } } void bogosort(int *a, int n) { while ( is_sorted(a, n) ) shuffle(a, n); } int main() { int numbers[] = { 1, 10, 9, 7, 3, 0 }; int i; bogosort(numbers, 6); for (i=0; i < 6; i++) printf("%d ", numbers[i]); printf("\n"); } C++[editar | editar código-fonte]
#include <algorithm> #include <vector> template<class T> void bogosort(std::vector<T>& array) { while (! is_sorted(array)) std::random_shuffle(array.begin(), array.end()); } template<class T> bool is_sorted(const std::vector<T>& array) { for (typename std::vector<T>::size_type i = 1; i < array.size(); ++i) if (array[i] < array[i-1]) return false; return true; } Java[editar | editar código-fonte]
public static void bogoSort(int length, int range) { int []array = randomIntArray(length,range); while (! isSorted(array)) array = randomArray(array); for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) { System.out.print(array[i] + " "); } } private static boolean isSorted(int [] array) { for (int i = 0; i < (array.length - 1); ++i) { if (array[i] > array[i+1]) return false; } return true; } private static int [] randomArray(int [] array) { int size = array.length; int[] indices = new int[size]; for (int i=0; i<size; i++) { indices[i] = i; } Random random = new Random(); for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { boolean unique = false; int nRandom = 0; while (!unique) { unique = true; nRandom = random.nextInt(size); for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) { if (indices[j] == nRandom) { unique = false; break; } } } indices[i] = nRandom; } int [] result = new int[size]; for (int k = 0; k < size; k++) { result[indices[k]] = array[k]; } return result; } private static int[] randomIntArray(int length, int n) { int[] a = new int[length]; Random generator = new Random(); for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) { a[i] = generator.nextInt(n); } return a; } Pascal[editar | editar código-fonte]
program bogosort (input, output); const max=10; {*Tamanho do vetor *} type vetor=array[1..max] of integer; var lista, lista1: vetor; i: integer; j: boolean; pos: integer; function teste(var proto: vetor): boolean; {*Verifica se o vetor NÃO está ordenado.*} var i: integer; begin teste:=true; for i:=2 to max do if (proto[i]<proto[i-1]) then break; if (i=max) and (proto[max]>=proto[max-1]) then teste:=false; end; begin randomize; {*Inicializa o gerador de numeros aleatórios *} writeln('Escreva abaixo os ', max,' elementos do vetor:'); for i:=1 to max do begin read(lista[i]); lista1[i]:=lista[i]; end; for i:=1 to max do {*Escreve o vetor recebido *} write(lista1[i],' '); writeln; while teste(lista1) do {*Enquanto o vetor nao esta ordenado...*} begin j:=true; for i:=1 to max do {*Inicializa o vetor auxiliar *} lista1[i]:=0; for i:=1 to max do {* Este loop preenche aleatoriamente o vetor auxiliar *} begin j:=true; while j do {* Este while garante que nenhum dado será sobrescrito *} begin pos:= random(max)+1; {* Gera posição aleatória *} if lista1[pos]=0 then {*Garante que a posição não está ocupada *} begin lista1[pos]:=lista[i]; j:=false; end; end; end; for i:=1 to max do {* Imprime na tela a tentativa *} write(lista1[i],' '); writeln; end; write('A LISTA FOI ORDENADA!'); end. Perl[editar | editar código-fonte]
use List::Util qw(shuffle); sub bogosort { my @a = @_; my @sorted = sort @a; while("@a" ne "@sorted") { @a = shuffle(@a); } return @a; } Python[editar | editar código-fonte]
import random def bogosort(nums): def isSorted(nums): if len(nums) < 2: return True for i in range(len(nums) - 1): if nums[i] > nums[i + 1]: return False return True while not isSorted(nums): random.shuffle(nums) return nums num1 = input('Input comma separated numbers:\n').strip() nums = [int(item) for item in num1.split(',')] print(bogosort(nums)) Ruby[editar | editar código-fonte]
def bogosort(seq) seq.shuffle! while not seq.each_cons(2).all? {|a,b| a <= b} end Fluxograma[editar | editar código-fonte]
Ver também[editar | editar código-fonte]
Referências
- ↑ «Python Data Structures and Algorithms: Sort a list of elements using Bogosort sort». w3resource (em inglês). Consultado em 24 de setembro de 2021