Superior rectus muscle
 From Wikipedia the free encyclopedia
From Wikipedia the free encyclopedia
| Superior rectus | |
|---|---|
 View of the eye from above, showing the action of the superior rectus muscle. | |
| Details | |
| Origin | annulus of Zinn at the orbital apex |
| Insertion | 7.9 mm superior to the corneal limbus |
| Nerve | oculomotor nerve |
| Actions | elevation, adduction, intorsion |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | musculus rectus superior bulbi |
| TA98 | A15.2.07.010 |
| TA2 | 2042 |
| FMA | 49035 |
| Anatomical terms of muscle | |
The superior rectus muscle is a muscle in the orbit. It is one of the extraocular muscles. It is innervated by the superior division of the oculomotor nerve (III). In the primary position (looking straight ahead), its primary function is elevation, although it also contributes to intorsion and adduction. It is associated with a number of medical conditions, and may be weak, paralysed, overreactive, or even congenitally absent in some people.

Structure[edit]
The superior rectus muscle originates from the annulus of Zinn. It inserts into the anterosuperior surface of the eye. This insertion has a width of around 11 mm.[1] It is around 8 mm from the corneal limbus.[1]
Nerve supply[edit]
The superior rectus muscle is supplied by the superior division of the ipsilateral oculomotor nerve (III). Each superior rectus muscle is innervated by contralateral oculomotor nucleus in the mesencephalon.[2]
Relations[edit]
The superior rectus muscle is related to the other extraocular muscles, particularly to the medial rectus muscle and the lateral rectus muscle.[3] The insertion of the superior rectus muscle is around 7.5 mm from the insertion of the medial rectus muscle, around 7.1 mm from the insertion of the lateral rectus muscle, and around 7.9 from the corneal limbus.[1] There is an intermuscular septum between it and the lateral rectus muscle.[3]
Variation[edit]
Variations of the superior rectus muscle is rare.[4] It may rarely have two muscle bellies parallel to each other.[4] More rarely, it may be congenitally absent.[5][6]
Function[edit]
The superior rectus muscle elevates, adducts, and helps intort (rotate the superior pole of the eye medially) the eye.
Clinical significance[edit]
Testing[edit]
The superior rectus muscle is the only muscle that is capable of elevating the eye when it is in a fully abducted position.[7]
Exophthalmos[edit]
Much of the venous drainage of the orbit and the extraocular muscles passes close to the superior rectus muscle.[8] Obstruction to this venous drainage can cause venous congestion in the eye, which may cause exophthalmos (bulging eye ball).[9] This may be shown with CT scans.[8]
Weakness and paralysis[edit]
The superior rectus muscle may be weakened or paralysed by problems with nerve conduction of the oculomotor nerve (III).[9] This may be congenital, often with a familial genetic link, or acquired, most often caused by head injuries.[9]
Overreaction[edit]
Local anaesthetics used in cataract surgery may weaken the inferior rectus muscle, despite efforts to use minimal anaesthetic and to avoid placing the needle into the muscle.[10] Weakness of the inferior rectus muscle may strengthen the superior rectus muscle, causing it to be overreactive.[10] This may elevate the eye, and prevent its use in normal vision.[10] Treatment may involve eye surgery that weakens or repositions the superior rectus muscle, which generally has good outcomes.[10]
Absence[edit]
Very rarely, the superior rectus muscle may be congenitally absent. This may be caused by Apert syndrome.[5] This causes a reduced ability to elevate the eye.[6] It may be treated with eye surgery that uses parts of the medial rectus muscle and the lateral rectus muscle to restore the functions normally performed by the superior rectus muscle.[6]
Additional images[edit]
This gallery of anatomic features needs cleanup to abide by the medical manual of style. |
- The right eye in sagittal section, showing the fascia bulbi (semidiagrammatic).
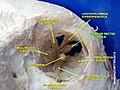
- Superior rectus muscle
- Superior rectus muscle
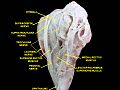
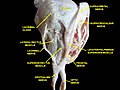
- Extrinsic eye muscle. Nerves of orbita. Deep dissection.
- Extrinsic eye muscle. Nerves of orbita. Deep dissection.
- Extrinsic eye muscle. Nerves of orbita. Deep dissection.
- Extrinsic eye muscle. Nerves of orbita. Deep dissection.
- Extrinsic eye muscle. Nerves of orbita. Deep dissection.
- Extrinsic eye muscle. Nerves of orbita. Deep dissection.
- Extrinsic eye muscle. Nerves of orbita. Deep dissection.
- Extrinsic eye muscle. Nerves of orbita. Deep dissection.
References[edit]
- ^ a b c Apt, L (1980). "An anatomical reevaluation of rectus muscle insertions". Transactions of the American Ophthalmological Society. 78: 365–375. ISSN 0065-9533. PMC 1312149. PMID 7257065.
- ^ Anderson, B.C.; McLoon, L.K. (2010), "Cranial Nerves and Autonomic Innervation in the Orbit", Encyclopedia of the Eye, Elsevier, pp. 537–548, doi:10.1016/b978-0-12-374203-2.00285-2, ISBN 978-0-12-374203-2, retrieved 2023-02-02
- ^ a b Nam, Yong Seok; Park, Yooyeon; Kim, In-Beom; Shin, Sun Young (2019-07-10). "Detailed Anatomy of the Lateral Rectus Muscle-Superior Rectus Muscle Band". Journal of Ophthalmology. 2019: e5374628. doi:10.1155/2019/5374628. ISSN 2090-004X. PMC 6652029. PMID 31360544.
- ^ a b Nayak, Satheesha B.; Shetty, Surekha D.; Kumar, Naveen; Aithal, Ashwini P. (2019-06-01). "Double-bellied superior rectus muscle". Surgical and Radiologic Anatomy. 41 (6): 713–715. doi:10.1007/s00276-019-02211-0. ISSN 1279-8517. PMID 30847519. S2CID 71147157.
- ^ a b Cuttone, James M.; Brazis, Peter J.; Miller, Marilyn T.; Folk, Eugene R. (1979-11-01). "Absence of the Superior Rectus Muscle in Apert's Syndrome". Journal of Pediatric Ophthalmology & Strabismus. 16 (6): 349–354. doi:10.3928/0191-3913-19791101-04. PMID 521875.
- ^ a b c Mather, Thomas R.; Saunders, Richard A. (1987-11-01). "Congenital Absence of the Superior Rectus Muscle: A Case Report". Journal of Pediatric Ophthalmology & Strabismus. 24 (6): 291–295. doi:10.3928/0191-3913-19871101-06. PMID 3320326.
- ^ "Eye Theory". Cim.ucdavis.edu. Retrieved 2012-12-02.
- ^ a b Hudson, Henry L.; Levin, Lori; Feldon, Steven E. (1991-10-01). "Graves Exophthalmos Unrelated to Extraocular Muscle Enlargement: Superior Rectus Muscle Inflammation May Induce Venous Obstruction". Ophthalmology. 98 (10): 1495–1499. doi:10.1016/S0161-6420(91)32099-2. ISSN 0161-6420. PMID 1961633.
- ^ a b c White, James Watson (1933). "Paralysis of the Superior Rectus Muscle". Transactions of the American Ophthalmological Society. 31: 551–584. ISSN 0065-9533. PMC 1315454. PMID 16692992.
- ^ a b c d Grimmett, Michael R.; Lambert, Scott R. (1992-07-01). "Superior Rectus Muscle Overaction After Cataract Extraction". American Journal of Ophthalmology. 114 (1): 72–80. doi:10.1016/S0002-9394(14)77415-X. ISSN 0002-9394. PMID 1621788.
External links[edit]
- Anatomy figure: 29:01-02 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center
- "Diagram". Archived from the original on March 25, 2010.