R. H. Elam
 From Wikipedia the free encyclopedia
From Wikipedia the free encyclopedia
Robert H. Elam | |
|---|---|
 "Notice", Natchez Daily Courier, February 10, 1852 | |
| Born | c. 1820 Tennessee |
| Died | after 1864 Unknown |
| Other names | R. H. Elam |
| Occupation | Slave trader |
| Years active | 1845?–1864 |
Robert H. Elam (c. 1820 – after 1864), usually advertising as R. H. Elam, was an American interstate slave trader who worked in Tennessee, Kentucky, Louisiana, and Mississippi.
Biography[edit]
Elam was born about 1820 in Tennessee.[1] According to a 1934 study of the interstate slave trade, Elam both exported slaves from Kentucky to the Deep South, and "served as a local broker for the small traders from the Blue Grass."[2] Elam may have served as a local broker in Mississippi for Kentucky traders Griffin & Pullum.[3]
As a property-owning white adult male, Elam was legally permitted to participate in democratic processes in the U.S. state of Mississippi in the early Republic era, and as such, he seemingly ran for office in 1845, coming in third in a three-way election for Wilkinson County circuit clerk.[4] In September 1850 he placed in runaway slave ad in a Nashville newspaper:
"$200 REWARD. Ran away from the undersigned, near Murfreesborough, Tenn., on the 3d instant, 2 Negro Men, namely: JOE, a Mulatto, 23 years old, straight black hair, 6 feet 2 inches high, and weighs about 180 pounds; had on a suit of red jeans, cloth cap, and a pair of new brogans. Also, boy JOHN, black complexion, 20 years old, 5 feet 7 inches high; weighs about 165 pounds; has a scar over the right ear in the hair; had on a black cloth coat, tow pants, and a new red wool hat. I will give 25 each, if taken in this State; 50 each, if taken in Kentucky; or 100 each, if taken in any other State. R. H. ELAM. Murfreesboro. Tenn., Sept. 11 Louisville Journal will copy to amount of $5 in daily and weekly paper, and charge to this office. Nashville Whig."[5]
Elam reported that he had been burglarized and offered a reward for some non-human lost property in an advertisement placed in the Mississippi Free Trader in 1851.[6] Elam would pay for the "recovery of all or any" of the missing items and pay a "$50 additional reward for the detection of the thief."[6][a]
STOLEN on the night of the 3d instant, my room at the Forks of the Road, near Natchez, was entered and the following property taken, viz: a small Calfskin POCKET BOOK, nearly new, containing a Spanish doubloon and a one dollar note on some one of the Tennessee banks; about eight dollars in silver, which was loose in my pocket; also, a plain Gold Lever Watch, with the letters "R. H. E." engraved on the back, made by James G. Bradley, Liverpool, No. 179, with a heavy Gold Vest Chain; also, a plain Silver Lever Hunting Watch, belonging to J. Q. Webb, besides various other small articles of less value.[6]
According to Frederic Bancroft in Slave-Trading in the Old South, Elam was one of the "best known" traders operating at the Forks of the Road slave market in Natchez, Mississippi in 1852–53.[7] One of Elam's ads from this era was highlighted in Harriet Beecher Stowe's coverage of the interstate slave trade in A Key to Uncle Tom's Cabin: "I have just returned to my stand, at the Forks of the Road, with fifty likely young NEGROES for sale."[8]
In 1853 Elam successfully sued the Adams County sheriff over a slave sales tax.[9] By proving that he had a slave depot in a fixed location rather than traveling from "point to point" selling slaves as the tax law described, he was able to avoid paying "three and one-eighth percent, upon the gross amount of sales, making, upon each slave of the value of $1,200, the sum of $37.50."[10] There were several similar suits pending in the courts, but Elam's was made the test case.[10] By the end of the 1850s Elam was operating out of the state capital, Jackson, Mississippi, but seemingly as a satellite to his main office in New Orleans.[11] In 1860, Elam and Walter Campbell were unique among slave traders advertising in New Orleans papers in that "their advertisements made no reference to the terms of sale," unlike the ads of others who specified that cash or a form of credit called "city acceptances" were both accepted.[12] Also in 1860 Griffin & Pullum advertised that they were selling out of the "old Elam House" at Forks of the Road.[13]

In 1858, Elam listed for sale his 365-acre (148 ha; 0.570 sq mi) property near Edgefield, outside of Nashville. Previously the property of Josiah Williams, it stood along the Gallatin Turnpike, and the Nashville and Louisville, and Edgefield and Kentucky Railroad ran through it. The property boasted "out-buildings, stables, cow-houses and poultry-yard, the splendid fish-pond, and excellent spring, fine garden and orchard," along with 100 acres of timberland and 190 acres in cultivation. The property was to be subdivided into smaller lots, and Elam's farm equipment and stock would be sold in early 1859.[14]
Elam paid for the treatment of 75 enslaved people at the Hôtel-Dieu hospital in New Orleans between 1859 and 1864.[15] It was profitable for traders to treat sickly enslaved people who had arrived "at their destinations physically and emotionally exhausted, often hungry and suffering from various illnesses—rather less attractive physical specimens than slave traders described in their advertisements for the purpose of making a sale."[16]
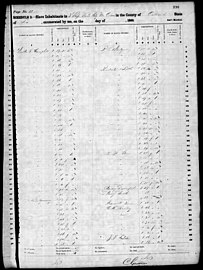
At the time of the 1860 federal census, Elam resided in New Orleans. His occupation was listed as "slave depot" and he reported owning $20,000 in real estate and owning $9,000 in personal property.[1] Elam was listed as the owner of seven people on the slave schedules that year, ranging in age from 11 to 35.[17] His slave depot was on the same street (possibly the same block of Baronne Street) as traders Poindexter & Little and Walter Campbell.[1][17][18]
The Henry Ford, in Dearborn, Michigan, holds bill of sale dated February from Elam for February 19, 1861 for four enslaved people, Harvey, Jack Tweet, Ambrose, and Henry Hindes for US$5,100 (equivalent to $172,947 in 2023) to Daniel Morrison.[19] The state of Louisiana had recently seceded from the Union and the words United States of America were struck out by the notary.[19] Elam's last known newspaper ad, which appeared April 9, 1861, three days before the firing on Fort Sumter, read "Please call at No. 58 Baronne Street, where planters and others will at all times find a carefully selected and assorted lot of SLAVES for sale. R. H. ELAM."[20] When the U.S. Army recaptured and occupied New Orleans in 1862, Elam fled to Tennessee.[21]
Additional images[edit]
- "For Sale—40 Choice Negroes", Natchez Daily Courier, December 14, 1849
- Elam's stand at the Forks of the Road was depicted on a 1856 surveyor's map
- Baronne Street slave jails on the 1860 slave schedules, including enumeration of people incarcerated on the premises of R.H. Elam
- Slave dealers in the 1861 New Orleans city directory
- Slave depot advertisements in the New Orleans Crescent in January 1861
See also[edit]
- List of American slave traders
- William A. Pullum – American slave trader (~1809–1876)
- History of slavery in Tennessee
- History of slavery in Kentucky
- History of slavery in Louisiana
- History of slavery in Mississippi
- Female slavery in the United States
Notes[edit]
- ^ For another "lost items" notice from a slave trader, see Theophilus Freeman's newspaper ad seeking the return of papers stolen from him in Richmond, Virginia.
References[edit]
Citations[edit]
- ^ a b c "Entry for R H Elam and James Wilson, 1860", United States Census, 1860 – via FamilySearch
- ^ Clark (1934), p. 337.
- ^ McDaniel (2019), p. 106.
- ^ "Wilkinson County—Election of County Officers". The Semi-Weekly Mississippi Free Trader. Natchez, Miss. November 13, 1845. p. 2. Retrieved 2023-11-28.
- ^ "$200 Reward". The Courier-Journal. September 10, 1850. p. 2. Retrieved 2023-11-28.
- ^ a b c "Stolen, on the night of the 2d instant". The Mississippi Free Trader. Natchez, Miss. April 9, 1851. p. 3. Retrieved 2023-11-28.
- ^ Bancroft (2023), p. 305.
- ^ Stowe (1853), p. 358.
- ^ Cushman, John F. (1855). "Samuel V. Newman v. Robert H. Elam". Reports of Cases Argued and Determined in the High Court of Errors and Appeals for the State of Mississippi, Volume XXVII. Vol. IV: Containing All the Cases Determined by the December Special Term, 1853, and Part of Those at the April Term, 1854. Boston: Little Brown & Co. pp. 474–476.
- ^ a b "Important Decision of the High Court". Vicksburg Whig. Vicksburg, Miss. April 5, 1854. p. 2. Retrieved 2023-11-28.
- ^ Bancroft (2023), p. 310.
- ^ Tadman (1977), pp. 240–241.
- ^ Betts, Vicki (2016), "Selected articles from the Natchez Daily Free Trader, published in Natchez, Mississippi, from February 4, 1860 through September 28, 1860, and February 16, 1861.", By Title, University of Texas at Tyler
- ^ "The Best Bill Yet—Maple Wood for Sale". Republican Banner. October 22, 1858. p. 3. Retrieved 2023-11-28.
- ^ Kenny (2010), p. 37.
- ^ Kenny (2010), p. 38.
- ^ a b "Entry for R H Elam, 1860", United States Census (Slave Schedule), 1860 – via FamilySearch
- ^ Gardner's New Orleans directory for 1861: including Jefferson City, Gretna, Carrollton, Algiers, and McDonogh : with a new map of the city, a street and levee guide, business directory, an appendix of much useful information, and a planters directory containing the names of the cotton and sugar planters of Louisiana, Mississippi, Arkansas and Texas : a summary of the commercial history of New Orleans, continued. New Orleans: Compiled and published by C. Gardner. 1861. p. 489. hdl:2027/dul1.ark:/13960/t5n880n68. Retrieved 2023-11-29 – via HathiTrust.
- ^ a b "Bill of Sale for African-American Slaves Bought from Robert Elam by Daniel Morrison, New Orleans, Louisiana, February 19, 1861", The Henry Ford Digital Collections, Dearborn, Mich., Object ID 92.0.112.3, retrieved 2023-11-28
- ^ "Please call at No. 58 Baronne Street". The Times-Picayune. April 9, 1861. p. 3. Retrieved 2023-11-28.
- ^ Colby, Robert K. D. (2024). An Unholy Traffic: Slave Trading in the Civil War South. Oxford University Press. p. 69. doi:10.1093/oso/9780197578261.001.0001. ISBN 9780197578285. LCCN 2023053721. OCLC 1412042395.
Sources[edit]
- Bancroft, Frederic (2023) [1931, 1996]. Slave Trading in the Old South (Original publisher: J. H. Fürst Co., Baltimore). Southern Classics Series. Introduction by Michael Tadman (Reprint ed.). Columbia, S.C.: University of South Carolina Press. ISBN 978-1-64336-427-8. LCCN 95020493. OCLC 1153619151.
- Clark, T. D. (December 1934). "The Slave Trade between Kentucky and the Cotton Kingdom". The Mississippi Valley Historical Review. 21 (3): 331–342. doi:10.2307/1897378. JSTOR 1897378.
- McDaniel, W. Caleb (2019). Sweet Taste of Liberty: A True Story of Slavery and Restitution. New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0190846992. LCCN 2018047090.
- Kenny, Stephen C. (2010). ""A Dictate of Both Interest and Mercy"? Slave Hospitals in the Antebellum South". Journal of the History of Medicine and Allied Sciences. 65 (1): 1–47. doi:10.1093/jhmas/jrp019. ISSN 0022-5045. JSTOR 24631845. PMID 19549698.
- Stowe, Harriet Beecher (1853). A key to Uncle Tom's cabin: presenting the original facts and documents upon which the story is founded. Boston: J. P. Jewett & Co. LCCN 02004230. OCLC 317690900. OL 21879838M.

- Tadman, Michael (1977). Speculators and slaves in the old South: a study of the American domestic slave trade, 1820-1860 (Thesis). University of Hull.