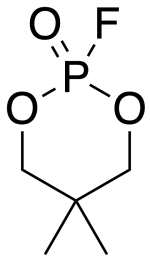
Neopentylene fluorophosphate
 From Wikipedia the free encyclopedia
From Wikipedia the free encyclopedia
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name 2-Fluoro-5,5-dimethyl-1,3,2λ5-dioxaphosphinan-2-one | |
| Other names NPF, neopentylene phosphoryl fluoridate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H10FO3P | |
| Molar mass | 168.104 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 41–42[1] °C (106–108 °F; 314–315 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Neopentylene fluorophosphate, also known as NPF, is an organophosphate compound that is classified as a nerve agent.[2][3] It has a comparatively low potency, but is stable and persistent, with a delayed onset of action and long duration of effects.[4]
See also[edit]
References[edit]
- ^ Edmundson R. Dictionary of Organophosphorus Compounds. pp 435-436. ISBN 9780412257902
- ^ Hart GJ, O'Brien RD, Milbrath DS, Verkade JG (1976). "Dissociation and phosphorylation constants for the inhibition of acetylcholinesterase by 2-fluoro, 2-oxo-1,3,2-dioxaphosphorinanes". Pesticide Biochemistry and Physiology. 6 (5): 464–470. doi:10.1016/0048-3575(76)90057-2. ISSN 0048-3575.
- ^ Crippin JB (2006). Explosives and Chemical Weapons Identification. Taylor & Francis. p. 21. ISBN 978-0-8493-3338-5.
- ^ Ledgard J (2006). A laboratory history of chemical warfare agents (2nd ed.). ISBN 978-0-6151-3645-5.